Comparative Analysis of RFID Windshield Tags and RFID Tire Tags in Automotive Security and Asset Management
In the rapidly evolving automotive industry, RFID technology has emerged as a cornerstone for enhancing security, traceability, and operational efficiency. Two specialized applications—RFID windshield tags and RFID tire tags—serve distinct yet complementary roles. This article explores their advantages, limitations, and unique functionalities in automotive management.
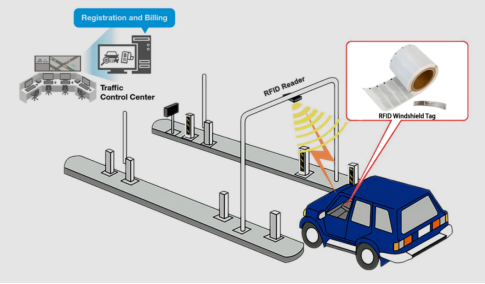
RFID Windshield Tags: Strengths and Applications
RFID windshield tags are engineered for seamless integration into vehicle management systems. Their anti-tear design, featuring precision-cut patterns, ensures that any unauthorized removal or tampering leaves visible damage, rendering the tag useless. This "one-tag-one-vehicle" principle is critical for preventing fraud and unauthorized reuse.
Key advantages include:
-
Long-range readability: These tags enable hands-free identification at distances of several meters, even at high speeds, making them ideal for automated toll collection, parking access, and fleet tracking.
-
Durability: Resistant to water, dust, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations, they maintain functionality in harsh environments.
-
High data capacity: Storing vehicle-specific details like VIN, ownership history, and maintenance records, they streamline compliance checks and audits.
Applications span access control in secured facilities, automated inventory management for dealerships, and real-time monitoring of logistics fleets.
RFID Tire Tags: Strengths and Applications
RFID tire tags are embedded during manufacturing to endure extreme conditions like high-pressure vulcanization and prolonged road stress. Their fragile substrate design ensures disintegration upon removal, deterring counterfeiters from transferring tags to illicit products.
Key advantages include:
-
Tamper-evident security: The combination of fragile materials and encrypted data storage prevents tampering and ensures authenticity.
-
Lifecycle tracking: From production to retreading, these tags store data on manufacturing dates, tread wear, and performance metrics, aiding quality control and sustainability initiatives.
-
Heat and pressure resistance: Built to withstand tire manufacturing and operational stresses, they ensure reliability across the product lifespan.
Applications focus on supply chain traceability, warranty validation, and optimizing retreading processes by monitoring tire health.

Contrasting Roles in Security and Functionality
While both tags prioritize anti-counterfeiting, their operational focus differs:
-
Windshield tags excel in dynamic, large-scale vehicle identification (e.g., highway tolling, border control) due to rapid read speeds and long-range capabilities.
-
Tire tags specialize in static, granular asset tracking (e.g., factory-to-dealer logistics, recycling compliance) by embedding directly into products for immutable data linkage.
Anti-Tampering Mechanisms
-
Windshield tags rely on physical fragility—any removal attempt shreds the tag, leaving clear evidence of tampering.
-
Tire tags combine embedded placement and cryptographic authentication to ensure data cannot be replicated or altered without authorization.
Conclusion
RFID windshield and tire tags address different facets of automotive security and efficiency. Windshield tags streamline high-speed, contactless vehicle management, while tire tags provide end-to-end visibility into product lifecycles. By integrating these technologies, businesses can achieve robust anti-fraud measures, operational transparency, and compliance with evolving industry standards.
For more details on RFID windshield tags, visit RFID Windshield Tag Solutions.
